If your work relies on continuous internet connectivity. You need reliable hardware, internet connection and power supply. An Uninterruptible Power Supply (or UPS) is an essential piece of hardware that ensures continuous and stable power supply to your workstation or office. A common question among users and prospective purchases is how long does a UPS last for your workstation setup? And how to calculate a battery life using a UPS runtime formula?
The battery life of a UPS device is principally dependent on two factors: (1) The capacity of the UPS battery and (2) the load requirements of devices connected to the UPS . If you want to calculate the runtime of a UPS the best and most accurate method is to use manufacturers discharge curves.
In this post I will explain the theory behind calculating the UPS runtime formula and how best to select a UPS for your needs using manufacturers discharge curves.
What is an Uninterruptible Power Supply?
An Uninterruptible Power Supply is a battery backup (usually lithium-ion) which provides power to connected devices when their power source fails.
Power failure can be a simple power outage or some other factor that might cause voltage to drop below the acceptable level. Some UPS devices are also designed to protect against power surges.
The UPS works as a bridge between the power source and the powered devices, and starts working only when power drops below a set level. Being a small device, a Uninterruptible Power Supply can power your computer, internet or other devices for a limited time. Typically enough time to power down devices or in some cases enough to wait for power to return.
Why use a UPS?
When doing important, connection sensitive work via the internet, being connected becomes indispensable.
An Uninterruptible Power Supply comes is almost essential for everyone who relies on continuous connectivity. Loss of connectivity can cause the loss of unsaved project work, loss of data feed in a live trading situation or unreliable communication.
An Uninterruptible Power Supply is also very useful in locations with erratic and unreliable power supplies. A UPS can help to smooth out any momentary loss in supply.
The loss of power, even for a couple of seconds, can become a catastrophe for those who work on live applications. The fear of suddenly going offline is a real fear particularly among day traders. Also occupations such as brokers, web developers, online teachers, and any profession that require uninterrupted internet connection.
In these cases, an Uninterruptible Power Supply, is an essential piece of workstation hardware.
Important UPS Specifications
When selecting the right UPS for your needs there are several key specifications to consider.
The three most important specifications are Battery Capacity and two power capacity ratings – VA and Watts. These are important to understand:
- Battery Capacity (AH) – Battery capacity is the measure of the charge stored in the battery. Measured in Amp-hrs (AH)
- VA Power Rating (VA) – VA is the maximum charge of the battery. The ‘VA’ represents the limit of power of the UPS will accept. It is measured is VA (Volts*Amps).
- Watts Power Rating (W) – This is the real power of the UPS. Measured in Watts (W), the unit for power. The Watts rating of the UPS is what you are actually power output of the UPS.
Refer to the short video clip below to understand the key differences between VA and Watts.
Other specifications worth considering are:
- Power connection – A UPS has a male AC connector, which is connected into a AC (Alternating Current) wall socket, powering the device and charging the battery.
- Power Outlets – Each UPS has a number of power outlets. The number of outlets will depend on the number of devices you want powered.
- Surge protection – Some UPS devices function as a means to protect your devices from electrical surge. Avoiding damage to your electrical equipment.
How long does a UPS last?
There are two three factors that determine how long a UPS battery will last:
- Battery Capacity (AH) – The Battery capacity a measure of the charge stored in the battery and is typically measured in Amp-hrs (AH). It is defined as the number of hours that the battery can deliver a current at the voltage of the battery.
- Power Load of devices being supported (W) – Each device to be supported by the UPS has their own power supply requirements. This is measured in Watts (W). The total load to be supported by the UPS is the sum of all these individual device power requirements.
- DC Bus (V) – Is the voltage required by the inverter to operate. DC buses range from 12V (1 x battery) to 180V (40 x batteries).
Battery capacity determines how long does a UPS last under load. The amount of power supplied by the Uninterruptible Power Supply at any one time will determine the life of a battery.
Other considerations:
The life of a UPS battery depends on a variety of factors. These factors include:
- Power factor – This is a fraction between 0 and 1 which represents the load current that provides useful energy to the devices. For many devices current flows into and then back to the battery without delivering power to equipment. The power factor accounts for the difference between VA and Watt power ratings. For any calculations use the Watts power rating.
- UPS efficiency – Not all battery capacity is available to run the load. Some battery energy is lost in cabling and connections. Also Inverters uses some of the battery energy to run internal electronics. Inefficiencies can be accounted for using an efficiency factor. e.g 70%. Also keep in mind that as batteries age they loss the capacity to deliver full load over time.
- Battery type – Important note: There are a huge range of battery types available. Different batteries discharge at varying rates. At higher loads batteries discharge exponentially faster than at lower loads.
Important Note: For an accurate estimate of battery life its important to refer to manufacturers discharge curves.
In the following sections I will explain how to estimate runtime of any UPS based on a simple UPS runtime formula. I’ll then elaborate on this calculation for how to better determine the runtime on specific Uninterruptible Power Supply devices based on individual manufacturer calculations.
UPS runtime formula
The UPS runtime formula can be used to estimate if the number of devices can be supported for the length of time needed.
UPS runtime formula calculates runtime based on the battery capacity and the total load on the UPS.
UPS runtime is a ratio of battery capacity (AH) over load (A) on the UPS:
Time = AH / A
How to calculate ups runtime formula | UPS selection calculation
The first thing I want to reiterate is the following calculations are for theoretical purposes. they are intended as a GUIDE ONLY. Any formula used to calculate Uninterruptible Power Supply runtime is based on several assumptions. These calculations do not account for UPS efficiencies or battery types – Batteries vary significantly between manufacturers. For an accurate estimate of battery life always refer to individual manufacturers discharge curves and recommendations.
How to calculate theoretical runtime using a UPS runtime formula
First identify all critical devices to backup. For example computer, monitors and an internet router and modem.
Next determine the power requirements of each device. Check each devices technical specifications. Often device power requirements aren’t listed in Watts. But instead a voltage and current are listed instead.
Check your devices label or technical specifications for power consumption (Watts).
Some manufacturers will list wattage for their devices. If not just look for the input voltage and current. These values might come in AC or DC (Direct Current). AC values usually have high voltages (the usual is 120V or 240V, depending on the country) and low currents. DC usually have low voltages, and slightly higher currents.
The following formula calculates power consumption (Watts) of each device based on the Voltage (V) and current (A) requirements:
W=V x A (Watts=Volts x Amps) (1)
The total load (Wt) of all devices is the sum of the power consumption (Watts) of all devices.
Wt = W1 +W2 + W3+… (2)
To calculate the amperage of load (A), re-arranging formula (1) above:
A = Wt / V (3) where V = DC battery voltage e.g 12 V
The run time of a UPS device is the ratio battery capacity (AH) over total load (A).
Time = AH / A (4)
Theoretical Example: If you have a setup that consists on a desktop computer that consumes 120W, two 70W monitors, and a 10W internet modem. Adding those quantities you need 270W for that system.
If you had a UPS with a 12V battery, battery capacity of 2.9AH and Watts Power Rating of 300W. We know that that the Uninterruptible Power Supply can support the load demand of 270W since it’s less than the Watts Power Rating of 300W.
We can calculate the amperage of the load on the UPS from formula (3). 270W / 12V = 22.5A.
Therefore the UPS runtime expected would be 2.9AH/22.5A = 0.13hrs or 7 minutes 44 secounds.
Keep in mind that this calculation doesn’t account for several other considerations listed above such as Uninterruptible Power Supply inefficiencies or battery type variations.
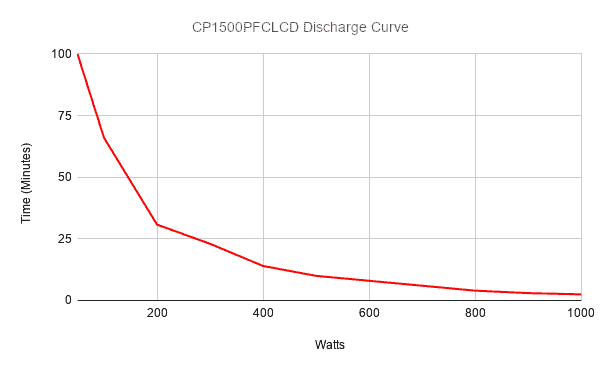
For this and a better more accurate calculation of UPS runtime use manufacturers UPS discharge curves:
How to calculate runtime using a manufacturers UPS discharge curves | Best UPS selection calculation
Practical example:
For a more accurate estimate of how long does a UPS last. Use manufactures discharge curves. The following is a summary of how to determine Uninterruptible Power Supply runtime using discharge curves.
This example uses the Cyberpower CP1500PFCLCD Uninterruptible Power Supply
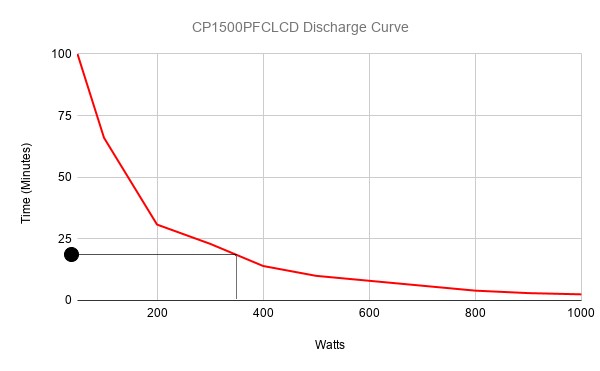
- Calculate total load in Watts from all devices connected to the UPS. Refer formula (2) above. For this example lets use 350W load from all devices.
- Refer to manufacturers discharge curve.
- Interpolate runtime from Load on discharge curve.
- Runtime is estimated as 20 minutes.
Best Uninterruptible Power Supplies
The following are some of my favorite Uninterruptible Power Supply devices on the market. These Uninterruptible Power Supplies are perfect for a home workstation setup.
Cyberpower CP1500PFCLCD
Cyberpower CP1500PFCLCD is perfect as a single workstation redundancy solution. It provides enough time to close out open positions and shutdown your system down safely.
Its perfect for areas with frequent power fluctuations. The Automatic voltage regulation corrects for minor fluctuations. Meaning you can trade with reduced risk in a live environment.
It can deliver up to 900W of power. Perfect for lots of devices or a few larger ones. It comes with 10 power outlets in total. All have surge protection. 5 of these outlets are backed up to battery.
Cyberpower CP1500PFCLCD Manufacturers discharge curve